What is Today’s Moon Phase?
In contemporary society, understanding the current moon phase is integral for various cultural, agricultural, and astronomical applications. To determine today’s moon phase, several resources and tools are readily available. For those seeking immediate information, specialized websites dedicated to lunar phases can provide real-time updates. Websites like timeanddate.com and moonphases.com offer interactive tools that display the current moon phase based on geographical location. Users simply need to input their location to receive accurate details about the moon’s appearance tonight.
Mobile applications also serve as convenient resources for moon phase tracking. Apps such as “Moon Phase” and “Lunar Phase” provide alerts and detailed information on the lunar cycle, making it easier for users to plan activities aligned with the moon’s visibility. These applications go beyond mere observations; they often include information on how each phase can affect various activities, from gardening to fishing, thus enhancing one’s relationship with natural cycles.
The significance of the moon phase extends far beyond mere aesthetics. Many agricultural practices are informed by lunar cycles, with some farmers choosing to plant or harvest based on moon phases believed to influence crop growth. In cultural practices, moon phases often hold symbolic meanings, with phases associated with different spiritual practices. The new moon, for example, is often a time for reflection and new beginnings, whereas the full moon invites celebrations and illumination.
For those wishing to observe the moon phase in their area, planning ahead is essential. Utilizing local weather forecasts to check for cloud cover can ensure optimal viewing. Observers can track the moon’s position in the sky, acknowledging that its appearance and visibility change daily, influenced by the ongoing lunar cycle. Understanding today’s moon phase will enhance the experiences of both seasoned astronomers and casual stargazers alike.
The Science Behind Moon Phases
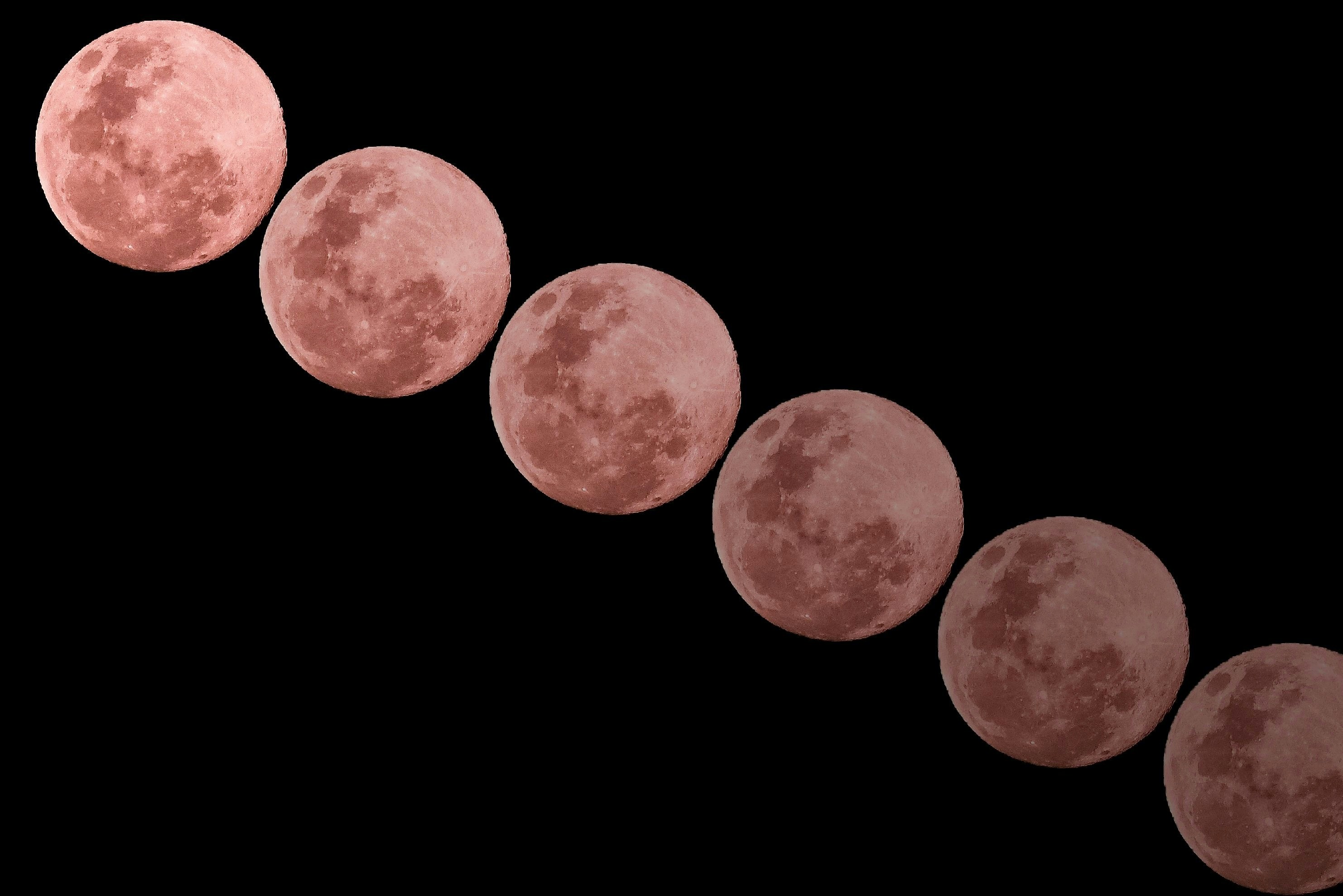
The moon displays various phases throughout its lunar cycle, a phenomenon resulting from its orbital mechanics and positional relationships with the Earth and the sun. As the moon orbits Earth, sunlight illuminates different portions of its surface, creating the distinct phases that are observed from our planet. Understanding this cycle is crucial for grasping why the moon appears differently at various times.
A lunar month consists of eight primary phases: new moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, last quarter, and waning crescent. These phases correspond to the moon’s position relative to the sun and Earth. For instance, during the new moon phase, the moon is positioned between the Earth and the sun, making it invisible from our vantage point. As it moves along its orbit, more of its illuminated surface becomes visible, leading to the waxing phases, where the moon’s brightness gradually increases.
<pconversely, 29.5=”” aids,=”” among=”” and=”” approximately=”” as=”” at=”” between=”” can=”” celestial=”” concepts.
Thus, the science of moon phases is grounded in astrological geometry and the predictable orbits of these celestial bodies. By comprehending the changing appearances of the moon, enthusiasts gain insight into both lunar dynamics and the broader astronomical context in which they reside.
Lunar Phases in 2025: A Calendar Overview
In 2025, the moon will undergo a series of distinct phases that will be observable from Earth, each influencing tides, animal behavior, and even human activities. Understanding these lunar phases offers valuable insight into their occasional ties to important astronomical events. This section provides a detailed calendar overview of the moon’s phases throughout the year, focusing on key dates for new moons, full moons, and the transitions between gibbous, crescent, and other stages.
In January, the year will start with a new moon on the 11th, followed by a full moon on the 25th. February will also present a new moon on the 9th and a full moon on the 24th. Moving into the spring months, March will feature a new moon on the 10th, with a full moon occurring on the 25th. Notably, March’s full moon is often referred to as the “Worm Moon.” April’s lunar activities include a new moon on the 8th and a full moon on the 23rd, the latter being termed the “Flower Moon.”
The middle of the year will see significant lunar phases as well. May will present a new moon on the 7th and a full moon on the 23rd, known as the “Strawberry Moon.” June will maintain this trend with a new moon on the 6th and a full moon on June 21st, which will also coincide with the summer solstice. Moreover, 2025 will witness a penumbral eclipse on March 25th, uniquely coinciding with the full moon.
As the year progresses into the latter half, July will see a new moon on the 5th and a full moon on the 21st. This pattern continues, with new moons on August 4th and August 19th for the full moon, termed the “Sturgeon Moon.” The transitions leading to the new moons and full moons will also be influenced by varying gibbous and crescent phases. Significant options for stargazers are available with the moon’s natural rhythm in September, October, November, and December, showcasing a full lunar cycle continually shaping our natural world.
Cultural Significance and Traditions Related to Moon Phases
The moon has held a profound influence on various cultures throughout history, serving as a guiding light for their calendars, festivals, and spiritual beliefs. Different civilizations have attributed diverse meanings to lunar phases, with the new moon and full moon often heralding significant moments in religious and agricultural practices. For instance, agrarian societies have long relied on the lunar cycle to dictate planting and harvesting times, believing that the moon’s gravitational pull affects growth cycles. The influence of lunar phases on soil moisture and warmth has led many farmers to follow lunar calendars in their agricultural endeavors.
In numerous cultures, specific festivals align with lunar phases. The Hindu festival of Diwali, often termed the “Festival of Lights,” coincides with the new moon, representing the triumph of light over darkness. Similarly, the Mid-Autumn Festival, celebrated in various East Asian cultures, occurs on the full moon in the eighth month of the lunar calendar. This event not only signifies harvest time but also emphasizes family reunions and lunar reflection. Such traditions illustrate how the moon phase significantly contributes to communal identity and cultural practices.
Moreover, lunar aspects play a consequential role in spirituality and folklore across the globe. In many Indigenous cultures, the moon is revered as a deity or is considered sacred, representing cycles of life and renewal. Folklore often includes myths involving the moon that convey morals or explain natural phenomena. These narratives have been handed down through generations, establishing an enduring connection to the rhythms of nature. Understanding the significance of lunar phases today can enhance our appreciation of heritage and traditions, highlighting the moon’s lasting impact on human culture and the natural world.